1) Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the molecule responsible for energy transfer in all organisms. The energy transfer takes place when ATP reacts with water in the presence of a biological catalyst called an enzyme. The resulting reaction forms adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and H3PO4:
Enzyme
ATP + H20(l) <==> ADP + H3PO4
As a catalyst, the enzyme participates in the reaction but is not consumed by it.
The Virtual Lab stockroom contains aqueous solutions of ATP as well as the enzyme catalyst for this reaction. Use the Virtual Lab to determine the enthalpy of this reaction. (Note the ATP is in an aqueous solution, so adding water is not necessary. The components on the left side of the chemical reaction are already combined in the solutions available to you, but nothing will happen without the enzyme. Assume that the specific heat of the enzyme solution is the same as that of water, 4.184 J/g °C)
2) Using the information in the table below, calculate the enthalpy of the reaction by taking into account bond breaking and bond making. The chemical formulas for the reaction are shown below.
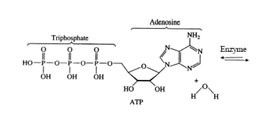
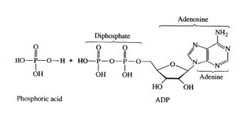
3) If we assume that the bond energies are the same for the O-H bonds in the reactants and products. Based upon your experimental results, what can you say about the difference in bond strength for the P-O bond from reactants to products?
4) When a biology textbook says "Energy is stored in ATP", how is it that this energy is stored? Please discuss. (It may be good to discuss this with your neighbors).